Automatic Image Captioning is the process by which we train a deep learning model to automatically assign metadata in the form of captions or keywords to a digital image.
Image captioning has various applications such as for annotating images, Understanding content type on Social Media, and specially Combining NLP to help Blind people to understand their surroundings and environment.

Table of Content
- Introduction to cAInvas
- Source of Data
- Data Visualization
- Feature Extraction and Data Preprocessing
- Model Training
- Introduction to DeepC
- Compilation with DeepC
Introduction to cAInvas
cAInvas is an integrated development platform to create intelligent edge devices. Not only we can train our deep learning model using Tensorflow, Keras, or Pytorch, we can also compile our model with its edge compiler called DeepC to deploy our working model on edge devices for production.
The Auto Image Captioning model is also developed on cAInvas and all the dependencies which you will be needing for this project are also pre-installed.
cAInvas also offers various other deep learning notebooks in its gallery which one can use for reference or to gain insight about deep learning. It also has GPU support and which makes it the best in its kind.
Source of Data
The data has been taken from kaggle which contains images along with its caption which is mostly a one line caption defining the image. We will define the dataset path by running the commands:
Data Visualization
For data visualization, we will use PIL library’s Image module. In this step, we will plot the image and print the caption in order to see whether the captions match with the image and also to gain intuition on what kind of data we are dealing with. Here is the image along with the caption.

For the captions, we will preprocess the text data such as we will create a dictionary for captions with an image file name as the key for the caption. Next, we will delete those captions which do not match with any image file name. Then we will add a keyword at the start and at the end of each caption. Here is an example of a caption:
"1000268201_693b08cb0e" : startseq child in pink dress is climbing up set of stairs in an entry way endseq
Feature Extraction and Data Preprocessing
Next step in the pipeline is to extract features from the image which we will pass into our auto captioning model. We won’t pass in the numpy array of the image rather we will use ResNet 50 to extract features from the images and then we will pass it into our captioning model. Then we will tokenize our captions and pad the caption text and once it is done we will create the trainset and testset.
Model Training
After creating the dataset next step is to pass our training data into our Deep Learning model to learn to caption the images. First, we will pass the extracted features of the images to an image model and then we will pass it to a language model. The final model architecture used is:
Model: "functional_7"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
embedding_input (InputLayer) [(None, 30)] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_input (InputLayer) [(None, 2048)] 0
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
embedding (Embedding) (None, 30, 128) 574336 embedding_input[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense (Dense) (None, 128) 262272 dense_input[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
lstm (LSTM) (None, 30, 256) 394240 embedding[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dropout (Dropout) (None, 128) 0 dense[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 30, 256) 0 lstm[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
repeat_vector (RepeatVector) (None, 30, 128) 0 dropout[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
time_distributed (TimeDistribut (None, 30, 128) 32896 dropout_1[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
concatenate_3 (Concatenate) (None, 30, 256) 0 repeat_vector[0][0]
time_distributed[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
lstm_7 (LSTM) (None, 30, 128) 197120 concatenate_3[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
lstm_8 (LSTM) (None, 512) 1312768 lstm_7[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 4487) 2301831 lstm_8[0][0]
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
activation_3 (Activation) (None, 4487) 0 dense_5[0][0]
==================================================================================================
Total params: 5,075,463
Trainable params: 5,075,463
Non-trainable params: 0
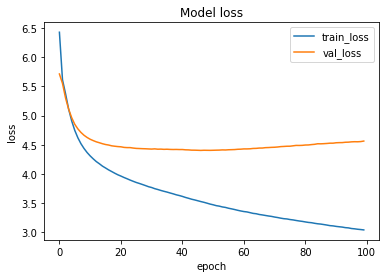
____________________________________________________________________The loss function used was “categorical_crossentropy” and optimizer used was “Adam”. For training the model we used Keras API with tensorflow at backend. Here is the training plot for the model:
Introduction to DeepC
DeepC Compiler and inference framework is designed to enable and perform deep learning neural networks by focussing on features of small form-factor devices like micro-controllers, eFPGAs, cpus, and other embedded devices like raspberry-pi, odroid, arduino, SparkFun Edge, risc-V, mobile phones, x86 and arm laptops among others.
DeepC also offers ahead of time compiler producing optimized executable based on LLVM compiler tool chain specialized for deep neural networks with ONNX as front end.
Compilation with DeepC
After training the model, it was saved in an H5 format using Keras as it easily stores the weights and model configuration in a single file.
After saving the file in H5 format we can easily compile our model using DeepC compiler which comes as a part of cAInvas platform so that it converts our saved model to a format which can be easily deployed to edge devices. And all this can be done very easily using a simple command.
And that’s it, our Auto Image Captioning Model is trained and ready for deployment.
Link for the cAInvas Notebook: https://cainvas.ai-tech.systems/use-cases/auto-image-captioning-app/
Credit: Ashish Arya
You may also be interested in
- Learning more about Road Crack Detection
- Reading about Parkinson’s Disease Detection using Spiral Drawings and CNN
- Also Read: Language identification of text — on cAInvas
- Finding out about Convolutional neural network, the brain-inspired algorithms revolutionizing how machines see and understand the world around us
Become a Contributor: Write for AITS Publication Today! We’ll be happy to publish your latest article on data science, artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and other technology topics.
